Continuous Compound Interest Vs Daily Compound Interst
What is Daily Compound Interest?
Daily compounded interest means interest is accumulated daily and is calculated by charging interest on principal plus interest earned daily; therefore, it is higher than interest compounded on a monthly/quarterly basis due to the high frequency of compounding.
Table of contents
- What is Daily Compound Interest?
- Formula
- Examples
- Relevance and Use
- Daily Compound Interest Video
- Recommended Articles
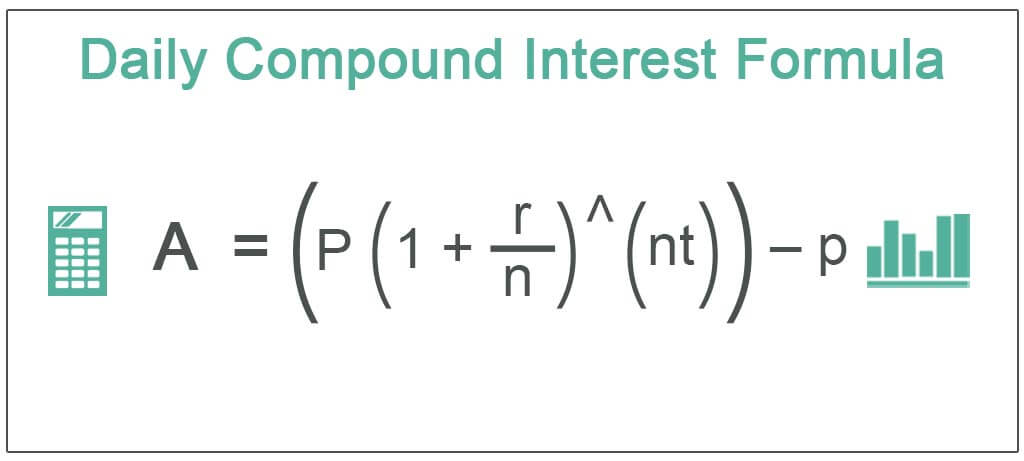
Formula
A=(P (1+r/n)^(nt)) – P
You are free to use this image on your website, templates, etc, Please provide us with an attribution link Article Link to be Hyperlinked
For eg:
Source: Daily Compound Interest (wallstreetmojo.com)
Where
- A=Daily compound rate
- P=Principal amount
- R=Rate of interest
- N=Time period
Generally, when someone deposits money in the bank, the bank pays interest to the investor in quarterly interest. But when someone lends money from the banks, the banks charge the interest from the person who has taken the loan in daily compounding interest. This scenario is mostly applicable in the case of credit cards.
Examples
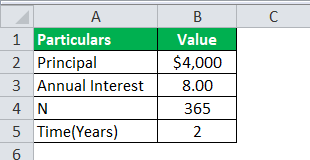
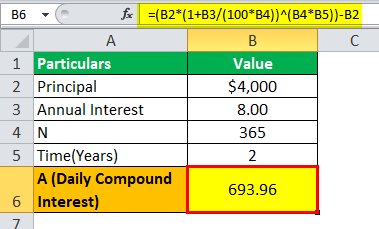
Example #1
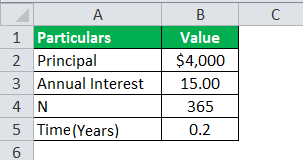
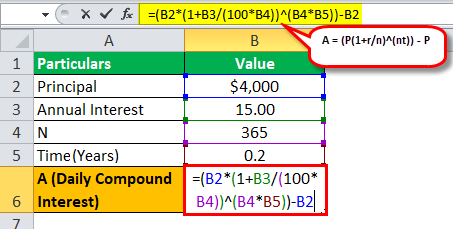
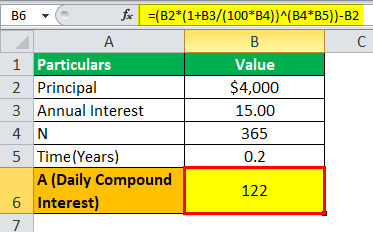
A sum of $4000 is borrowed from the bank, where the interest rate is 8%, and the amount is borrowed for two years. Let us determine how much will be daily compounded interest calculated by the bank on loan provided.
Solution:
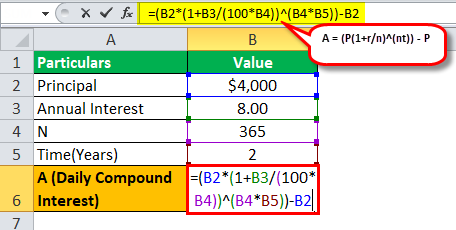
= ($4000(1+8/365)^(365*2))-$4000
Example #2
Daily compounding is practically applicable for credit card spending, which the banks charge to the individuals who use credit cards. Credit cards generally have a cycle of 60 days, during which the bank does not charge any interest, but interest is charged when the interest does not pay back within 60 days. If a sum of $4000 is used using a credit card by an individual for its spending. And the interest rate is 15% per annum as the interest charged for a credit card is generally very high. And the amount is repaid by the individual after 120 days, that is, 60 days after the grace period Grace periods are extra days given after the due date to undertake an unfulfilled obligation without penalties. They are a common instance in the financial world and are usually offered to clients who apply for a credit card, student loan, insurance, or mortgage to attract more customers. read more is over. So the individual needs to pay the bank interest for 60 days, and he is charged at a daily compounding rate.
Solution:
= $4000(1+15/365)^(365*(12/60))-$4000
Example #3
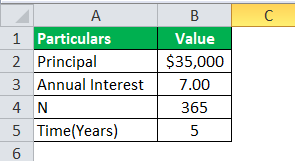
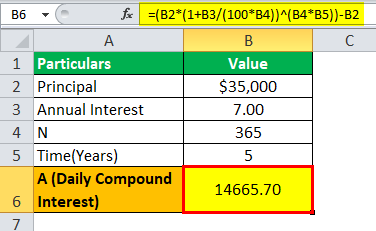
A sum of $35000 is borrowed from the bank as a car loan where the interest rate is 7% per annum, which is borrowed for five years. Let us determine how much will be daily compounded interest calculated by the bank on loan provided.
Solution:
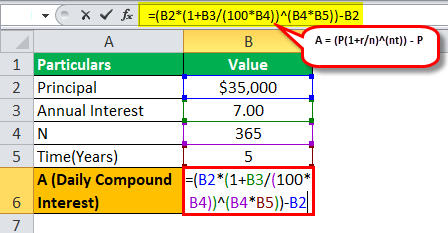
= ($35000(1+.07/365)^(365*5))-$35000
Relevance and Use
Generally, when someone deposits money in the bank, the bank pays interest to the investor in quarterly interest. But when someone lends money from the banks, the banks charge the interest from the person who has taken the loan in daily compounding interest. The higher the frequency, the more interest is charged or paid on the principal. It is how the banks make their money on the differential of the interest.
You can download this template from here – Excel Template
Daily Compound Interest Video
Recommended Articles
This article is a guide to Daily Compound Interest Formula. Here we discuss how to calculate daily compound interest using its formula and examples and a downloadable excel template. You can learn more about financial analysis from the following articles –
- Monthly Compound Interest Formula Monthly compound interest refers to the compounding of interest every month, which implies that the compounding interest is charged both on the principal and the accumulated interest. read more
- Formula The continuous compounding formula depicts the interest received when constant compounding is done for an infinite number of periods. The four variables used for its computation are the principal amount, time, interest rate and the number of the compounding period. read more of Continuous Compounding
- Simple Interest vs. Compound Interest Simple interest is calculated on principal amount that is borrowed or invested by a person. Whereas compound interest is calculated on the sum total of principal amount and previous period's accumulated interests. read more
- Formula The effective interest rate is the actual rate of interest earned or paid after compounding. It is determined as: Effective Annual Rate Formula = (1 + r/n)n – 1 read more of Effective Annual Rate
lindenbergyoultas.blogspot.com
Source: https://www.wallstreetmojo.com/daily-compound-interest/
Comments
Post a Comment